Bunion Exercises After Surgery
Overview
 A bunion is the enlargement of the joint at the base of the big toe. It occurs as a result of the misalignment of the bones of the big toe. This leads to stretching of the ligaments and tendons around the big toe joint and causes soft tissue over the joint to become inflamed and painful. There may be additional bone formation (exostosis) in the joint and the skin around the joint may become red and tender. Over time the cartilage in the joint can break down, leading to arthritis.
A bunion is the enlargement of the joint at the base of the big toe. It occurs as a result of the misalignment of the bones of the big toe. This leads to stretching of the ligaments and tendons around the big toe joint and causes soft tissue over the joint to become inflamed and painful. There may be additional bone formation (exostosis) in the joint and the skin around the joint may become red and tender. Over time the cartilage in the joint can break down, leading to arthritis.
Causes
There is much debate as to which is the major cause, but it is likely that your genetic makeup makes you more prone to a bunion or bunionette and that then wearing ill-fitting footwear causes them to develop. Studies have shown that in cultures where people don?t wear shoes but are habitually barefoot, there are very few cases of foot bunions indicating a strong correlation with shoe wear. They are more common in females, most likely due to choice of footwear.
Symptoms
The most obvious symptoms of a bunion are. Pain in the area of the MTP joint, the joint where your big toe connects to your foot. Bending of the big toe in towards the other toes. An enlarged bump of bone or tissue at the MTP joint. Each symptom can range in degree from small to severe. Sometimes the pain can be sufficient to make it difficult to walk in normal shoes. Other symptoms may include. Swelling and inflammation of the skin around the MTP joint. Thickening of the skin in the area of the joint. Restricted motion in your big toe. Pressure from the inward bending of your big toe can affect your other toes, leading to corns on your smaller toes. Ingrown toenails on the smaller toes. Development of hammertoes in the other toes. Calluses on the bottom of your foot. If you have any of these symptoms, especially pain, displacement of your big toe or development of a bulge, you should consider consulting your physician. Even if you're not significantly bothered by some of these symptoms, bunions tend to continue getting bigger and more serious over time and should be taken care of before they do so.
Diagnosis
Bunions are readily apparent, you can see the prominence at the base of the big toe or side of the foot. However, to fully evaluate your condition, the Podiatrist may arrange for x-rays to be taken to determine the degree of the deformity and assess the changes that have occurred. Because bunions are progressive, they don't go away, and will usually get worse over time. But not all cases are alike, some bunions progress more rapidly than others. There is no clear-cut way to predict how fast a bunion will get worse. The severity of the bunion and the symptoms you have will help determine what treatment is recommended for you.
Non Surgical Treatment
Padding with a number of different materials (eg felt) to reduce pressure on the painful prominence of the bunion. Physical therapy can be used to help with the symptoms and improve the range of motion (this is particularly helpful if the pain is coming from inside the joint, rather than from shoe pressure). Manipulation of the joint can be used to help with this (manipulation will never correct the alignment of the joint). Any corns and calluses that are causing symptoms should be treated. The correct fitting of footwear is essential for anyone who is serious about doing something about their bunions and hallux valgus. It may be possible to have your shoes stretched over the area of the bunion to also relieve pressure. Foot orthotics may be useful in helping with the instability about the joint. They may be more helpful if there are other symptoms in the foot as well, as their use in "treating" bunions is controversial. They may play a role in slowing progression and in the prevention of bunions developing again after surgical correction. Exercises can be important in maintaining the mobility of the joint in those with bunions, this is especially important for the arthritic type pains that may be originating from inside the joint and for the prevention of these painful symptoms in the future. 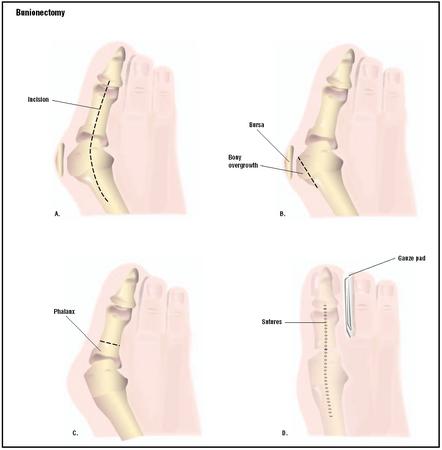
Surgical Treatment
Surgery may be considered if your symptoms are severe and don't respond to non-surgical treatments. The type of surgery will depend on the level of deformity, the severity of your symptoms, your age, and any other associated medical conditions.
Prevention
The best way to reduce your chances of developing a bunion is to wear shoes that fit properly. Any shoe that is too tight or too high will force your toes together and may cause the condition to develop. Shoes need to be wide enough, so they aren't rubbing against the joint, and preferably made of leather. Avoid shoes with a lot elaborate stitching at the front, as this can also cause irritation. Heels should be no more than three to four inches and you should only wear them occasionally. Court shoes should seldomly be worn, as they do not give the foot any support. Be honest with yourself, you know if your shoes aren't fitting you comfortably. Do something about it, or you will suffer for your vanity.